Introduction
In ancient times, people believed that diseases were caused by supernatural powers. They thought these diseases were sent by God as a form of punishment for their sins. Some thought that evil spirits enter the body and cause infections. Some attributed the astrological phenomenon to these diseases. Accordingly, people used to treat these diseases by praying to God and performing witchcraft to tame evil powers.
Humoral theory
The Greek physician Hippocrates, the father of medicine, ignored these beliefs. He observed people suffering from diseases and studied how health was influenced by diet and the environment. Through his studies, he believed in the Humoral theory. Humors refer to body fluids. The theory states that the human body consists of four body fluids. These fluids include Blood, Phlegm, Yellow bile, and Black bile. The humoral theory states that when the four humors are in perfect balance, the body remains healthy. Similarly, improper balance of these humors will result in some pain.
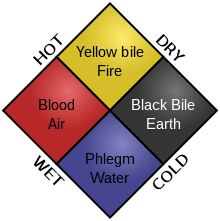
Therefore, for any individual to be healthy, all four humors must be in perfect balance. Any deficiency or excess release of these liquids will cause disease. Hippocrates established the humoral theory of medicine, which was focused on balancing these four humors. The cause of these humoral imbalances was attributed to the bad air. If a person is sick, the physician’s job is to bring back the balance of these liquids. There were multiple ways to restore the humoral imbalance, such as inducing vomiting, making incisions and bloodletting, enema, and changing the diet plans, etc. However, the diagnosis of the disease was based on this chart. This chart helped them understand what kind of treatment to provide. These four humors are associated with four different seasons, organs, temperaments, and elements of nature.
After several years, Galen’s medical investigations further supported the humoral theory. Because of his interest in human anatomy, he observed the bodies of people who died of diseases. As Roman law prohibited human dissection, he performed dissections on living monkeys and pigs. From ancient Greek times, the bad air was thought to be the cause of diseases like Cholera and Malaria. This bad air was called as Miasma. The bad air was considered to be poisonous, and it could be identified by its foul or rotten smell.
In 1348, when the Plague arrived at Catalonia, a Spanish physician, Jacme d’Agramount, educated the general public on the preventive measures to be taken against the disease. One of his statements to the public was to shut the windows to avoid exposure to the air.
Considering the effects of bad air, the British parliament passed a law in 1388 that said the deposition of dung, garbage, and killed animals into the surrounding waters is prohibited. The Miasma theory was accepted by the medical world for many centuries, as the diseases were rapidly spreading where there was a lot of foul smell. Therefore, all the preventive measures were based on restricting the bad smell in public places.
Investigation on Cholera
The real challenge was faced when the Cholera out broke in London in 1849. As London became more populous, the Thames River was polluted with sewage water. William Farr, a British government servant, stated in his report that Cholera was caused by polluted air, and the geographical elevation of the city was the major cause for the spread of the disease. However, the improved sanitary systems against the Miasma theory could not completely stop the disease’s spread.
During this period, John Snow, a British physician, studied the causes of Cholera and came up with the idea that contaminated water was the source of Cholera, not the polluted air. Snow’s logical explanation of Cholera spread by water could not convince William Farr, who was the leading board member of the General Health Committee, in 1854. Being a strong believer in the Miasma theory, William Farr was not in a position to accept the other mode of disease transmission.

Later, the continuous spread of Cholera made the scientists, including William Farr, re-examine Snow’s investigation. The final investigation concluded that the contaminated water supply was the cause of the Cholera spread. William Farr finally accepted John Snow’s explanation in 1866, by the time Snow was no longer alive.
The Miasma theory was gradually forgotten, and the Germ theory was brought to light.